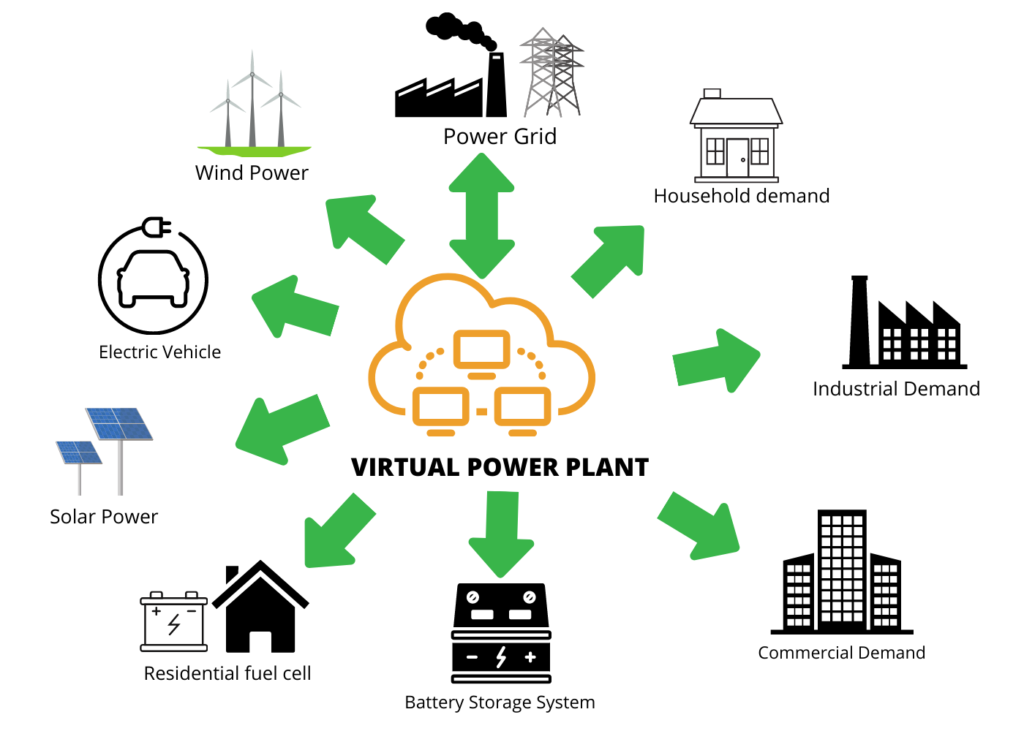
What is Virtual Power Plant (VPP), and principle of work? In recent years, virtual power plants (VPPs) have become increasingly popular as an alternative way to generate energy. A VPP is essentially a system of connected renewable energy sources that can be monitored and managed remotely in order to generate electricity. The distributed resources are often connected together over the internet and offer several advantages over traditional power plants. Let’s take a closer look at what a VPP is, how it works, and why it has become so popular.
What is a Virtual Power Plant?
A virtual power plant (VPP) is a network of distributed energy resources (DERs) that are connected and managed by software. These DERs can include solar panels, wind turbines, batteries, combustion engines, hydropower plants and other sources of renewable energy generation. By connecting these sources together with software, the VPP aggregates the output from each source into one larger source of electric power for delivery to customers or utilities. This aggregation allows for more efficient management of grid operations and increased reliability when compared to traditional methods of generating electricity from centralized power plants.
How Does It Work?
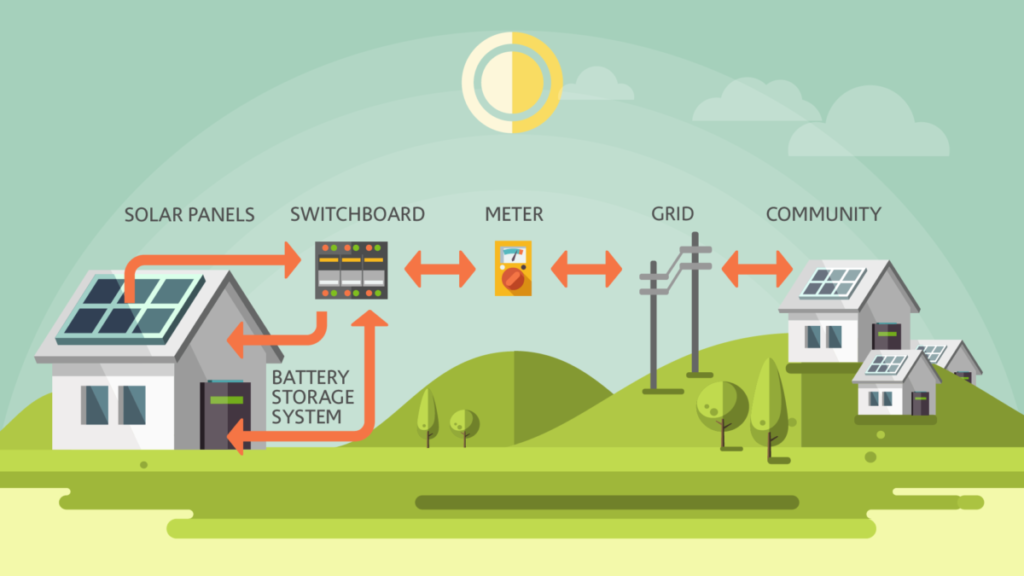
The main benefit of a virtual power plant (VPP) is its ability to aggregate multiple sources of renewable energy generation into one large source with the help of sophisticated algorithms that optimize the system’s performance. This aggregation allows for better control over electric supply and demand while also providing greater flexibility in terms of how much electricity can be generated at any given time. Additionally, since all the distributed resources are connected together via software, they can be monitored and managed remotely which reduces operational costs significantly.
Benefits of Using a virtual power plant (VPP):
One major benefit of using a Virtual Power Plant (VPP) is that it helps reduce emissions from traditional power generation methods such as burning coal or natural gas. By utilizing renewable energy sources such as solar or wind instead, emissions are significantly reduced which helps combat climate change as well as improve air quality in heavily populated areas where traditional power plants are located. Additionally, since most distributed resources do not require large amounts of land or infrastructure to set up compared to traditional power plants, they are often cheaper to install and maintain than their counterparts which makes them an attractive option for utilities looking to cut costs while still providing reliable electric service. Additionally, many countries offer incentives for implementing renewable energy sources such as tax breaks or rebates which further increase the cost savings associated with using virtual power plant (VPPs) versus traditional power plants. Lastly, because all the resources within the network can be monitored remotely and adjusted on demand through software-based algorithms, it leads to greater efficiency in terms of both cost saving measures as well as improved reliability for customers who rely on uninterrupted access to electricity throughout their day-to-day lives.
Conclusion:
Virtual Power Plants (VPPs) have become increasingly popular in recent years due to their ability to aggregate multiple sources of renewable energy generation into one large source with optimized performance levels when compared to traditional methods such as burning coal or natural gas for electricity production. Not only do VPPs help reduce emissions from electricity production but they also provide cost savings due to reduced installation requirements plus incentives provided by governments around the world who encourage investing in green technology solutions like this one. In addition, remote monitoring capabilities mean that utilities can better manage their electric supply while providing reliable service without interruption even during peak demand times when other forms electrical generation might not be able to meet customer needs quickly enough on its own – making virtual power plants an attractive solution worth exploring further by anyone interested in reducing costs while still providing reliable service at scale!


