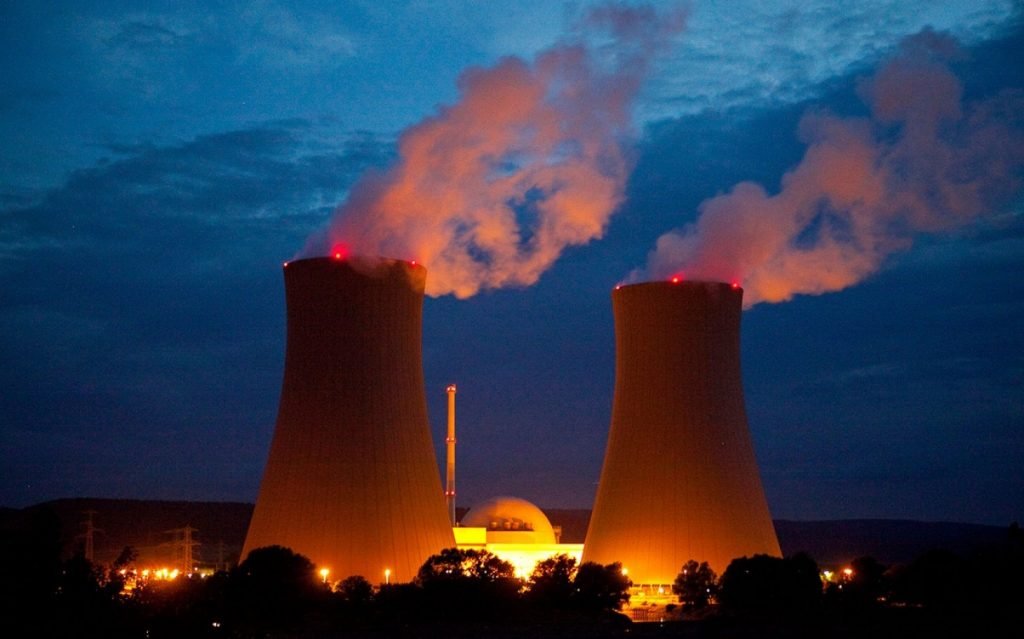

Nuclear power, also known as atomic energy, releases the dense nuclei of atoms in large quantities in proces involving atomic nuclei. The energy of other atomic physics, such as natural chemical reactions, is different and requires only atomic orbital electrons. The controlled nuclear fission in reactors that now operate in many parts of the world in electricity generation is one method of releasing nuclear energy. Another process, controlled nuclear fusion, has been planned, but not perfected by 2020. Nuclear fusion and nuclear fission have explosively released nuclear energy. See nuclear energy, too.
Is nuclear energy renewable? Is nuclear energy clean? In this article we are going to examine this questions and concepts.
The nucleus of an atom in nuclear fission like uranium or plutonium. It breaks into two lighter nuclei with approximately equal weight. In some cases , the process can occur spontaneously, or may be injected through excitation of the nucleus in the form of gamma rays, or through the use of a variety of particles (e.g. neutrons, protons, Deuteron or alpha parts). The fission process releases a large amount of energy, produces radioactive products and emanates several neutrons.

The neutrons can lead to fission in a close core of fissile material and release more neutrons that can repeat the sequence, causing a chain reaction in which many nuclei become fissured and a huge amount of energy is released. Such a chain reaction can provide power for society if controlled within a nuclear reactor. If uncontrolled, it can lead to an explosion of amazing destructive power, like the so-called nuclear bomb.
The process of Nuclear Fusion involves heavier components for nuclear reactions between light elements. In cases of elements of low nuclear numbers (Hydrogen [Atomic 1], or their deuterium and tritium isotopes), the interaction of nuclei releases considerable amounts of energy. The enormous energy potential of nuclear fusion was first used in thermal or hydrogen bombs that developed in the decades following World War II. The possible peaceful applications of nuclear fusion have been fostered, in particular with regard to the largely limitless supply of fusion fuel to earth.
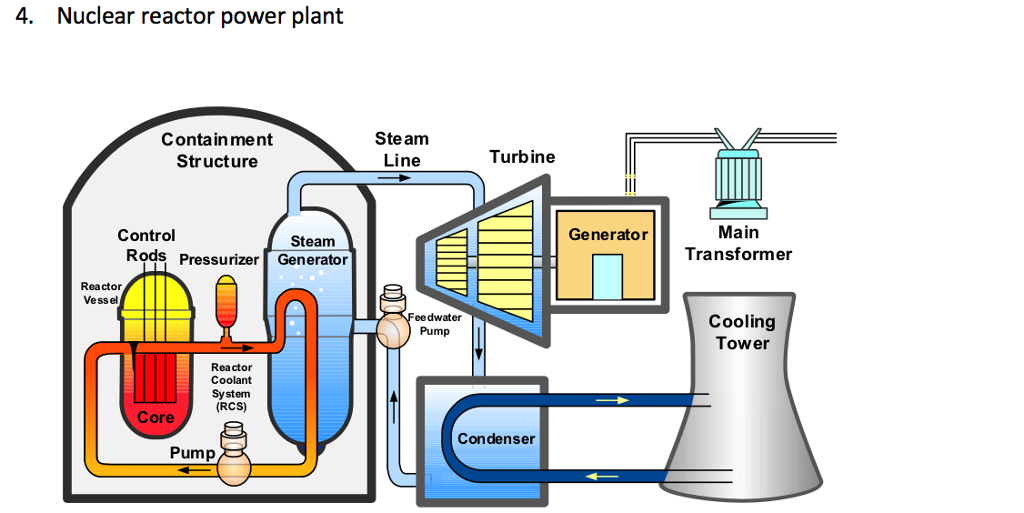
Although no practical fusion reactors have been constructed yet, the plasma temperature and heat isolation needed conditions were largely achieved, implying that fusion energy is now a serious possibility for generation of electricity. Commercial fusion reactors pledge a global supply of inexhaustible electricity.



thank you for this blog
merciii