The power industry represents an entire industry, including fuel extraction, manufacturing, refining and distribution, that is involved in the production and sale of energy.
Modern society uses vast quantities of fuel and in nearly all countries the energy sector is a critical part of society ‘s infrastructure and sustainability.

The energy industry in particular includes:
- the fossil fuel industries including the coal (extraction and processing) and natural gas industries (natural gas extraction, carbon production and distribution & sales), the oil industry, the oil companies, the manufacturing industries, fuel transportation and end user purchases at gas stations);
- Fossil-fuel industry, including the petroled (oil companies, oil refiners, fuel transport and final-use sales at gas stations) coal (extraction / processing) and natural-gas (natural, coal-fired, distribution and sales) industries;
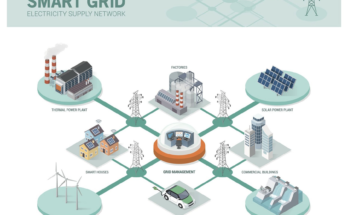
- The power generation, electricity distribution and sales industry; electrical power industry;
- the business of nuclear power;
- the renewable energy industry, consisting of alternative power providers and sustainable energy companies, including those engaged in the generation of hydroelectric power, wind , and solar energy; and,
- The traditional energy industry, focused on firewood harvesting and distribution, is especially popular in the poorest countries for use in cooking and heating.
The growing reliance in the 20th century on fossil fuel and nuclear energy during non-renewable sources means that the energy industry has also contributed significantly to environmental and pollution impacts. Fossil fuels have become the primary energy source in most parts of the world and have played a significant role in global warming and pollution. Most countries invest in clean and sustainable resources as part of human response to global warming.


One Comment on “Energy industry”