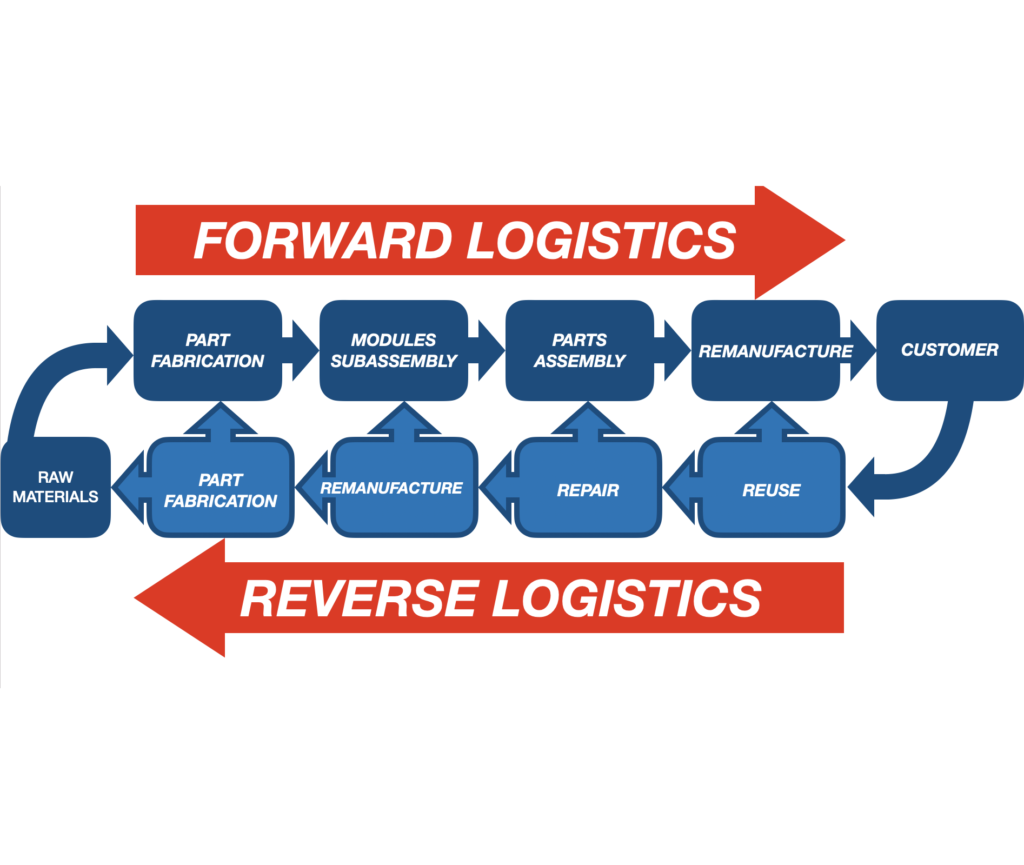
Definition of Reverse Logistics
Energy Efficiency in Reverse Logistics may seem like a complex subject. Before delving into Energy Efficiency in Reverse Logistics, we first need to explain reverse logistics. Reverse logistics refers to the process of planning, implementing, and controlling the efficient and cost-effective flow of goods, materials, and information from the end consumer back to the manufacturer or supplier. Unlike traditional logistics, which primarily focuses on the forward movement of goods from the manufacturer to the consumer, reverse logistics deals with the reverse flow of products for the purpose of returns, recycling, remanufacturing, or proper disposal. This process holds immense potential for reducing waste and environmental impact while optimizing resource use.
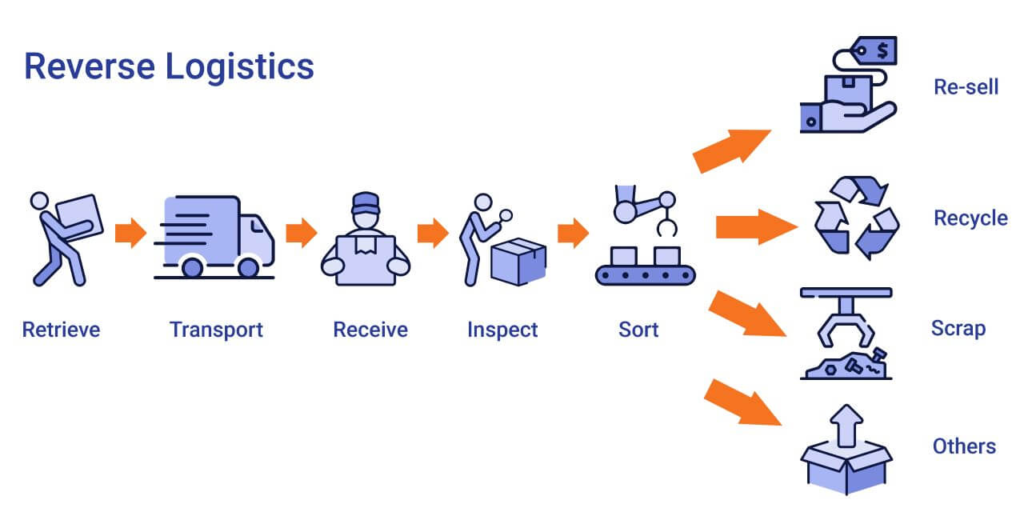
Significance of Energy Efficiency in Modern Business
Energy efficiency has emerged as a cornerstone of contemporary business operations. It encompasses the judicious management of energy resources to accomplish tasks with minimal waste. In today’s environmentally conscious world, energy efficiency is more than just a buzzword; it’s a strategic imperative. By enhancing energy efficiency, businesses not only reduce operational costs but also bolster their sustainability credentials. This is particularly pertinent in the context of reverse logistics, as the associated processes can have a substantial environmental footprint, which can be significantly reduced through energy-efficient practices.
Understanding Reverse Logistics: Unveiling Its Essence
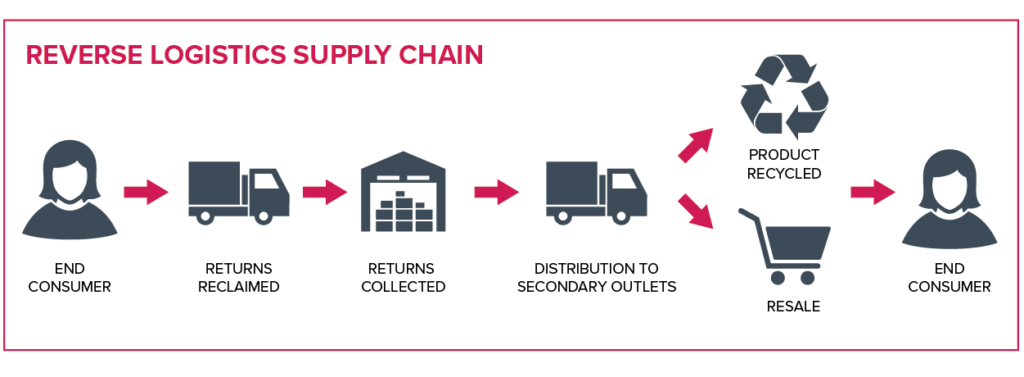
This section aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of reverse logistics by elucidating its definition, scope, key components, and the pivotal role it plays in fostering sustainability.
Defining Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics can be defined as the systematic process of planning, implementing, and overseeing the efficient and cost-effective flow of products, materials, and information in the opposite direction of the traditional supply chain. It encompasses all activities involved in the management of returned goods, recycling, remanufacturing, and appropriate disposal. The primary goal of reverse logistics is to optimize value recovery while minimizing waste, thereby contributing to economic, environmental, and social sustainability.
Exploring the Scope of Reverse Logistics
The scope of reverse logistics extends across various industries and sectors. It encompasses not only the handling of customer returns but also the management of end-of-life products, recycling programs, and the recovery of valuable materials. The reverse logistics process can involve a range of stakeholders, from consumers and retailers to manufacturers and third-party service providers. This comprehensive approach ensures that products and materials circulate efficiently through the supply chain, even after their initial use, thereby reducing waste and environmental impact.
Key Components of Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics comprises several key components:
- Returns Management: Handling the return of products from consumers, which may involve inspection, refurbishing, or recycling, based on the condition of the returned item.
- Remanufacturing: The process of restoring used products to like-new condition, thus extending their lifecycle and reducing the demand for new materials.
- Recycling and Waste Management: Responsible disposal of products or materials, aiming to minimize environmental impact through recycling, waste-to-energy conversion, or safe disposal in compliance with regulations.
- Inventory Management: Efficiently managing returned goods and end-of-life inventory, which includes decisions related to storage, transportation, and disposition.
- Collaboration: Effective communication and collaboration among various stakeholders, including consumers, retailers, manufacturers, and logistics providers, to ensure the seamless flow of products and information within the reverse logistics chain.
The Role of Reverse Logistics in Sustainability
Reverse logistics plays a pivotal role in promoting sustainability across various dimensions:
- Environmental Sustainability: By enabling the recycling and responsible disposal of products, reverse logistics reduces the environmental footprint associated with waste generation and landfill disposal. It also conserves resources and energy, aligning with the principles of the circular economy.
- Economic Sustainability: Efficient reverse logistics can generate cost savings by recovering and reusing valuable materials and components. This not only reduces production costs but also creates new revenue streams through remanufactured and recycled products.
- Social Sustainability: Responsible reverse logistics practices contribute to improved public and worker safety by ensuring proper disposal of hazardous materials. They also enhance brand reputation by demonstrating a commitment to ethical and sustainable business practices.
In conclusion, understanding reverse logistics is paramount in recognizing its substantial impact on sustainability. This section has shed light on its definition, scope, and key components, showcasing its significance in the context of modern business operations. The subsequent sections will delve deeper into the interplay between reverse logistics and energy efficiency, offering strategies and insights for achieving a sustainable and energy-efficient reverse logistics system.
Energy Efficiency and Its Environmental Impact in Reverse Logistics
This section will delve into the profound connection between energy consumption and reverse logistics, shedding light on the environmental ramifications of inefficient practices while emphasizing the multitude of benefits that stem from enhancing energy efficiency.
The Link Between Reverse Logistics and Energy Consumption
A direct correlation exists between energy consumption and the intricate world of reverse logistics. Traditional logistics and the movement of goods in the supply chain already demand substantial energy. Reverse logistics compounds this energy usage as it involves the transportation, sorting, refurbishing, and recycling of returned items. Inefficient reverse logistics practices can lead to increased energy consumption, which in turn heightens the carbon footprint of a business’s operations. Therefore, optimizing energy use in the reverse logistics process becomes crucial in mitigating environmental impact.
Quantifying Energy Use in Traditional Logistics
To fully appreciate the environmental implications of reverse logistics, it’s essential to comprehend the energy demands of traditional logistics. This includes the energy consumed in manufacturing, transportation, and warehousing, as well as packaging materials. A significant portion of these energy expenditures stems from fossil fuels, which release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change. When products are returned through reverse logistics, additional energy is expended in their transportation and handling. By quantifying the energy use in traditional logistics, businesses can grasp the potential for energy efficiency improvements.
Environmental Impact of Inefficient Reverse Logistics
Inefficient reverse logistics not only impacts a company’s bottom line but also has profound environmental consequences. When returned products are not handled optimally, they may end up in landfills, contributing to waste generation and environmental pollution. Inefficient disposal methods, such as incineration, can release harmful emissions into the atmosphere. Additionally, the energy-intensive nature of inefficient reverse logistics amplifies the carbon footprint, accelerating climate change. In essence, failing to manage the reverse logistics process efficiently results in a negative environmental legacy, perpetuating resource waste and pollution.
Benefits of Improving Energy Efficiency
Recognizing the adverse environmental effects of inefficient reverse logistics, businesses are increasingly motivated to enhance energy efficiency in their operations. There is a myriad of benefits associated with this endeavor:
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Improving energy efficiency in reverse logistics results in reduced energy consumption and, consequently, a diminished carbon footprint. This environmentally responsible approach aligns with global efforts to combat climate change and fosters a more sustainable future.
- Cost Savings: Energy-efficient practices lead to reduced operational costs. By optimizing transportation routes, minimizing energy use, and adopting sustainable packaging, businesses can save on fuel and energy expenses.
- Enhanced Brand Reputation: Consumers are increasingly environmentally conscious. Businesses that prioritize energy efficiency and sustainable reverse logistics practices can strengthen their brand reputation, attracting eco-minded consumers and differentiating themselves in the market.
- Compliance with Regulations: In many regions, there are strict regulations governing waste disposal and emissions. By improving energy efficiency and embracing sustainable practices, companies can ensure compliance with these regulations, avoiding legal issues and associated fines.
- Resource Conservation: Efficient reverse logistics processes promote resource conservation by enabling the recycling and reuse of materials. This not only reduces the need for virgin resources but also minimizes waste generation.
In conclusion, this section underscores the intricate relationship between energy efficiency, reverse logistics, and their environmental consequences. It illuminates the imperative of quantifying energy use in both traditional and reverse logistics while highlighting the profound benefits of improving energy efficiency. The subsequent sections will delve into specific strategies for achieving energy efficiency in reverse logistics, showcasing real-world case studies and exploring future trends in sustainable logistics practices.
Strategies to Boost Energy Efficiency in Reverse Logistics
This section unravels a spectrum of strategies designed to enhance energy efficiency in the realm of reverse logistics. We explore innovative approaches across transportation, warehouse operations, and technology integration.
Transportation Optimization for Energy Efficiency in Reverse Logistics
Efficient transportation is the linchpin of energy-efficient reverse logistics. It encompasses several aspects, each playing a vital role in reducing energy consumption and environmental impact:
- Optimal Routing: Employing sophisticated route planning software to determine the most fuel-efficient paths for transportation, thereby minimizing energy expenditure.
- Vehicle Load Consolidation: Maximizing the use of available space within vehicles to reduce the number of trips and fuel consumption. This often involves consolidating multiple shipments to minimize empty space.
Route Planning and Consolidation
Route planning and consolidation involve the meticulous organization of transportation routes to minimize energy waste and emissions. By employing advanced route planning software and consolidating deliveries, businesses can substantially reduce energy consumption, lower operational costs, and mitigate environmental impact.
Vehicle Selection and Eco-friendly Alternatives
Selecting the appropriate vehicles for reverse logistics is paramount. Many businesses are transitioning to eco-friendly alternatives, such as electric or hybrid vehicles, to reduce emissions. Additionally, optimizing the size and capacity of vehicles according to specific transportation needs can lead to energy savings. Businesses should continually evaluate their fleet to ensure it aligns with their energy efficiency goals.
Warehouse Operations
Efficient warehouse operations play a pivotal role in conserving energy. This includes:
- Efficient Inventory Management: Implementing a lean inventory management system that reduces the need for storage and transportation of excess stock. This not only saves energy but also lowers warehousing costs.
- Smart Packaging and Handling: Utilizing sustainable packaging materials that are both lightweight and recyclable. Efficient handling practices can reduce the energy expended in loading and unloading operations.
Technology Integration
The integration of advanced technologies is a game-changer in improving energy efficiency in reverse logistics. Key technologies include:
- IoT and Data Analytics: Leveraging the Internet of Things (IoT) for real-time tracking and monitoring of shipments. Data analytics help identify energy-saving opportunities and optimize processes.
- Automation and Robotics: Implementing automation and robotics in warehouse and distribution centers to streamline operations and reduce human labor, resulting in energy savings and increased accuracy.
Efficient transportation, route planning, vehicle selection, warehouse operations, and technology integration are integral aspects of energy-efficient reverse logistics. These strategies empower businesses to reduce energy consumption, lower costs, and bolster their environmental sustainability credentials. The subsequent section will delve into real-world case studies, illustrating the practical application of these strategies in diverse business contexts.
Case Studies: Exemplifying Energy Efficiency in Reverse Logistics
This section brings real-world insights into the realm of energy-efficient reverse logistics by examining three compelling case studies. These stories illustrate the successful implementation of sustainable practices in diverse business contexts.
Case Study 1: XYZ Company’s Energy-Efficient Reverse Logistics
XYZ Company, a leading electronics manufacturer, embarked on a journey to revamp its reverse logistics processes. Recognizing the significance of energy efficiency, the company sought to reduce its carbon footprint and operational costs. Their strategies included:
- Optimized Transportation: XYZ Company invested in a route planning system that minimized the travel distance for returned products, cutting down on fuel consumption and emissions. Vehicle load consolidation further reduced the number of trips.
- Eco-Friendly Fleet: The company replaced a significant portion of its delivery fleet with electric vehicles. This shift not only reduced emissions but also lowered fuel and maintenance costs.
- Recycling Initiatives: XYZ Company introduced an extensive recycling program to recover valuable materials from returned electronics. This not only reduced waste but also led to cost savings through material recovery.
These initiatives resulted in a significant reduction in energy consumption, a 25% decrease in reverse logistics costs, and a strengthened commitment to environmental sustainability.
Case Study 2: Green Packaging and Reverse Logistics Success
A global consumer goods company recognized that the environmental impact of its packaging was a critical aspect of reverse logistics. By transitioning to sustainable packaging materials and optimizing their handling and storage, they achieved remarkable results:
- Sustainable Materials: The company shifted to recyclable, lightweight packaging materials that reduced the weight and volume of their products. This decreased transportation costs and energy usage.
- Efficient Handling: Implementing more efficient handling practices in their warehouses minimized energy consumption during loading and unloading. This was achieved through automation and staff training.
- Consumer Awareness: The company also educated consumers about responsible disposal and recycling, encouraging them to return packaging materials for recycling, reducing waste in landfills.
This approach resulted in a 20% reduction in reverse logistics energy consumption and a notable reduction in waste generation, aligning with their sustainability goals.
Case Study 3: E-commerce Giants’ Innovative Practices
E-commerce giants, known for their complex reverse logistics networks, have implemented innovative practices to enhance energy efficiency:
- Return Centers: E-commerce leaders have established dedicated return centers strategically located to reduce the distance returned products need to travel. This approach minimizes energy consumption in transportation.
- Data-Driven Decisions: These companies harness data analytics and IoT technology to gain real-time visibility into their supply chains. This enables them to identify inefficiencies and make immediate adjustments to optimize energy use.
- Sustainable Packaging: Partnering with suppliers to adopt sustainable packaging solutions, these e-commerce giants have reduced waste and transportation costs. They also encourage recycling and responsible disposal among their customers.
The amalgamation of these strategies has translated into significant energy savings, reduced operational costs, and enhanced sustainability for the e-commerce giants.
These case studies collectively underscore the diverse approaches that organizations have taken to bolster energy efficiency in reverse logistics. The lessons drawn from these real-world examples can serve as inspiration and guidance for businesses seeking to embark on their own journey toward a more sustainable and energy-efficient reverse logistics system. In the following section, we will explore the challenges organizations might encounter in implementing energy-efficient practices and discuss potential solutions.
Overcoming Challenges in Implementing Energy-Efficient Reverse Logistics
This section delves into the challenges businesses often face when implementing energy-efficient practices in their reverse logistics processes. It examines regulatory hurdles, infrastructure limitations, change management, and workforce challenges, and explores the balancing act of initial investment versus long-term savings.
Regulatory Hurdles Energy Efficiency in Reverse Logistics
Regulations can pose significant challenges for companies looking to optimize their reverse logistics for energy efficiency. Different regions have varied rules governing waste disposal, recycling, and emissions. Ensuring compliance with these regulations while striving for energy-efficient operations can be a complex balancing act. Companies must invest in robust compliance management systems and stay abreast of evolving legislation to navigate these challenges successfully.
Infrastructure Limitations
Inefficient or outdated infrastructure can hinder the implementation of energy-efficient reverse logistics. Warehouses and distribution centers designed without energy efficiency in mind may lack essential features such as automation or optimal layout design. Adapting existing infrastructure to support energy-efficient practices may require substantial capital investment. Overcoming these limitations often involves a phased approach, prioritizing upgrades based on potential energy savings and return on investment.
Change Management and Workforce Challenges
Implementing energy-efficient reverse logistics practices often necessitates a shift in the organizational culture and workforce competencies. Change management is vital to ensure that employees adapt to new processes and technologies. Resistance to change can be a significant hurdle, but proper training, communication, and engagement can facilitate a smooth transition. Workforce challenges may also include finding skilled personnel capable of managing advanced technologies like IoT and automation.
Initial Investment vs. Long-term Savings
One of the primary challenges lies in the decision between allocating resources for initial investment in energy-efficient systems and realizing long-term savings. Some businesses may be hesitant to invest upfront in sustainable infrastructure and technologies, fearing the impact on profitability. However, a long-term perspective reveals that energy-efficient reverse logistics can significantly reduce operational costs and bolster environmental credentials. Balancing these short-term concerns with the long-term benefits is a challenge that requires careful financial planning and strategic vision.
Successfully navigating these challenges requires a holistic approach that combines regulatory compliance, infrastructure improvements, workforce development, and strategic financial planning. Despite the obstacles, the benefits of energy-efficient reverse logistics, including reduced energy consumption, lower operational costs, and enhanced sustainability, make the journey worthwhile.
In the next section, we will explore the tools and technologies available for monitoring and improving energy efficiency in reverse logistics, providing businesses with actionable solutions to address these challenges.
Tools and Technologies for Monitoring Energy Efficiency
This section delves into the invaluable tools and technologies available for monitoring and enhancing energy efficiency in reverse logistics. These advanced solutions empower businesses to track energy usage, assess their carbon footprint, and adhere to industry standards.
Energy Tracking and Reporting Systems
Energy tracking and reporting systems are fundamental for gaining real-time insights into energy consumption throughout the reverse logistics process. These systems employ sensors, meters, and data collection mechanisms to monitor energy use in transportation, warehousing, and other operations. The collected data is then analyzed to identify inefficiencies and areas where energy savings can be achieved.
By having a granular understanding of energy consumption, businesses can make data-driven decisions to optimize their processes. For example, they can identify vehicles with high energy consumption and replace them with more efficient alternatives, or fine-tune warehouse lighting and HVAC systems to minimize energy waste.
Carbon Footprint Assessment Tools
Measuring and mitigating the carbon footprint is a critical aspect of energy-efficient reverse logistics. Carbon footprint assessment tools provide businesses with the means to quantify the greenhouse gas emissions associated with their operations. These tools factor in various parameters, including energy usage, transportation, and waste generation, to provide a comprehensive view of the environmental impact.
By assessing their carbon footprint, companies can pinpoint the most significant sources of emissions and develop strategies to reduce them. This often involves optimizing transportation routes, adopting eco-friendly vehicles, and implementing recycling programs to minimize waste.
Benchmarking and Industry Standards
Benchmarking and adhering to industry standards are essential for gauging energy efficiency in reverse logistics. By comparing their performance to industry benchmarks and standards, businesses can identify areas where they may be falling short. This can also serve as a benchmark for improvement and a means to demonstrate commitment to sustainability.
Several organizations and industry groups have established standards and best practices for sustainable reverse logistics. Adhering to these standards not only provides a framework for energy-efficient practices but also enhances a company’s reputation and credibility in the eyes of customers and stakeholders.
These tools and technologies empower businesses to monitor their energy efficiency, reduce their carbon footprint, and align their operations with industry standards. By leveraging these solutions, companies can enhance their environmental sustainability and reduce energy costs, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable and efficient reverse logistics system.
In the following section, we will explore future trends and innovations in the realm of energy-efficient reverse logistics, providing a glimpse into what lies ahead for businesses seeking to stay ahead of the curve.
Future Trends and Innovations: Pioneering Sustainability in Reverse Logistics
This section delves into future trends and innovations that are set to reshape the landscape of energy-efficient reverse logistics. As we peer ahead, we witness the emergence of the circular economy, innovative sustainable packaging solutions, and the advent of carbon-neutral transportation.
Circular Economy and its Impact on Reverse Logistics
The concept of a circular economy is rapidly gaining traction across industries. It envisions a world where products are designed, produced, used, and returned for remanufacturing or recycling, creating a closed loop of resource utilization. In the context of reverse logistics, the circular economy implies a fundamental shift in how companies manage returned products.
The key impact is on product design. Items are being engineered for easier disassembly, component reuse, and material recycling. As this concept takes hold, reverse logistics will transition from merely managing returns to facilitating product regeneration. This shift can drastically reduce waste, lower energy consumption, and enhance resource efficiency.
Sustainable Packaging Solutions
Packaging plays a pivotal role in reverse logistics and can significantly influence energy efficiency. Forward-thinking companies are embracing sustainable packaging solutions that reduce waste and lower transportation energy costs. Key trends include:
- Lightweight Packaging: Designing packaging that is lighter in weight, reducing energy required for transportation and lessening the environmental impact.
- Reusable Packaging: Implementing packaging that can be reused multiple times before recycling, lowering waste and energy consumption.
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Utilizing biodegradable, compostable, and recyclable materials in packaging, thereby contributing to energy savings during disposal.
Sustainable packaging not only reduces environmental impact but also appeals to environmentally conscious consumers, enhancing brand reputation and attracting a loyal customer base.
Carbon-Neutral Transportation
The transportation industry is undergoing a transformation with the aim of achieving carbon neutrality. Companies are actively exploring and implementing alternative fuels, electric vehicles, and low-emission technologies to reduce the carbon footprint of their transportation operations.
In reverse logistics, carbon-neutral transportation is particularly promising. Emissions generated during product returns and recycling can be offset by using sustainable transportation methods. This approach includes the use of electric delivery vehicles, integrating carbon offsets, and adopting sustainable transportation practices. By embracing carbon-neutral transportation, businesses can make substantial strides in minimizing the environmental impact of their reverse logistics processes.
As the future unfolds, these trends and innovations are poised to revolutionize energy-efficient reverse logistics. By aligning with the principles of the circular economy, embracing sustainable packaging solutions, and adopting carbon-neutral transportation practices, businesses can not only enhance energy efficiency but also position themselves as leaders in sustainable, eco-friendly logistics.
In the concluding section, we will recap the benefits of energy efficiency in reverse logistics, emphasizing its far-reaching impact on businesses and the environment.
Benefits Beyond Energy Efficiency: Fostering Sustainability and Success
This section delves into the multifaceted benefits that extend far beyond energy efficiency when businesses embrace sustainable practices in reverse logistics. We explore how these practices enhance customer loyalty, brand image, ensure regulatory compliance, mitigate risks, and reinforce social responsibility and ethical business practices.
Enhanced Customer Loyalty and Brand Image
Energy-efficient reverse logistics significantly improve a company’s standing in the eyes of environmentally conscious consumers. By actively reducing their carbon footprint and promoting sustainable practices, businesses foster a loyal customer base. When customers perceive a company as socially and environmentally responsible, they are more likely to become repeat buyers, recommending the brand to others. Enhanced customer loyalty and a positive brand image translate into long-term profitability.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Mitigation
Implementing sustainable practices in reverse logistics ensures compliance with ever-evolving environmental regulations. Businesses that adhere to these regulations not only avoid costly fines and legal troubles but also create a risk-mitigation strategy. By embracing energy efficiency and environmentally responsible practices, companies safeguard their reputation and financial stability, minimizing potential risks and liabilities.
Social Responsibility and Ethical Business Practices Aiming Energy Efficiency in Reverse Logistics
Energy-efficient reverse logistics represent a commitment to social responsibility and ethical business practices. Beyond satisfying legal obligations, these practices resonate with a broader societal audience. Businesses that engage in environmentally friendly operations contribute to the broader effort to protect the planet, conserve resources, and promote responsible consumption. This commitment underscores their ethical stance, reinforcing their position as a responsible corporate citizen.
In conclusion, the benefits of energy efficiency in reverse logistics transcend the realm of operational cost reduction. By prioritizing sustainability, companies enhance their customer loyalty, bolster brand image, ensure regulatory compliance, mitigate risks, and champion social responsibility and ethical business practices. These benefits not only position businesses for long-term success but also contribute to a more sustainable, eco-conscious global community.
In the final section, we will recap the key takeaways of this article, reinforcing the significance of energy efficiency in reverse logistics and encouraging businesses to embrace sustainable practices for a brighter and more efficient future.
Conclusion: Paving the Way to a Sustainable Tomorrow
In closing, let’s recap the pivotal importance of energy efficiency in the realm of reverse logistics and emphasize the compelling reasons for businesses to wholeheartedly embrace sustainable practices.
The Importance of Energy Efficiency in Reverse Logistics
Energy efficiency in reverse logistics is not merely an operational choice; it’s a strategic imperative. It serves as a linchpin for reducing environmental impact, conserving resources, and optimizing costs. From the efficient management of product returns to the adoption of eco-friendly transportation and packaging solutions, the benefits are myriad. Companies that prioritize energy efficiency not only reduce their carbon footprint but also strengthen their brand image, ensure regulatory compliance, and foster customer loyalty.
Encouragement for Businesses to Embrace Sustainable Practices Implementing Energy Efficiency in Reverse Logistics
As we move into an era marked by heightened environmental consciousness, businesses must seize the opportunity to lead by example. Embracing sustainable practices in reverse logistics isn’t just about being responsible corporate citizens; it’s about thriving in a rapidly changing marketplace. By reducing energy consumption, lowering costs, and enhancing their environmental credentials, companies can secure a competitive edge, attract loyal customers, and ensure long-term success.
In a world where sustainability is no longer an option but a necessity, it’s time for businesses to embark on the path of energy-efficient reverse logistics. Let us seize this moment to not only shape a more efficient future but to pave the way for a truly sustainable tomorrow.
FAQs on Energy Efficiency in Reverse Logistics
Let’s address some common questions regarding energy efficiency in the context of reverse logistics:
What is the primary goal of reverse logistics?
The primary goal of reverse logistics is to efficiently manage the return, remanufacturing, recycling, and proper disposal of products and materials, thereby reducing waste and environmental impact, and optimizing resource use. It’s about creating a closed-loop system that maximizes value recovery while minimizing negative environmental consequences.
How does energy efficiency relate to sustainability in logistics?
Energy efficiency is integral to sustainability in logistics because it helps reduce the environmental footprint of transportation, storage, and handling processes. Sustainable logistics aims to balance economic, environmental, and social impacts. By minimizing energy consumption, companies lower emissions, conserve resources, and align with the principles of the circular economy.
What technologies can help monitor Energy Efficiency in Reverse Logistics?
Various technologies can assist in monitoring energy consumption in reverse logistics:
- Energy tracking and reporting systems: Utilize sensors and data analysis to monitor energy usage in transportation, warehousing, and other operations.
- IoT (Internet of Things): Provides real-time tracking and monitoring capabilities to assess energy use throughout the supply chain.
- Data analytics: Enables businesses to identify inefficiencies and energy-saving opportunities.
What are the key challenges when implementing energy-efficient reverse logistics?
Implementing energy-efficient reverse logistics may involve challenges such as regulatory hurdles, infrastructure limitations, workforce resistance to change, and the need for initial investments. Companies must navigate complex regulations, adapt existing infrastructure, manage workforce transitions, and balance short-term expenses with long-term savings.
Are there any government incentives for adopting energy-efficient practices in logistics?
Many governments offer incentives to encourage businesses to adopt energy-efficient practices. These incentives may include tax benefits, grants, subsidies, or credits for investing in sustainable technologies or achieving specific sustainability goals. Incentives vary by region and are often designed to promote environmental responsibility and resource conservation. Businesses should research available incentives to capitalize on these opportunities.


One Comment on “Energy Efficiency through Reverse Logistics: A Sustainable Solution”